
- Firstly, locating of tendons at several positions of the web of the box girder is performed by performing scans with GPR equipment. Mainly, 2D scans were executed at several testing areas in order to ensure that tendons are positioned properly. Since, tendons are located through GPR scans then evaluation of ducts can be performed. Each tendon is marked with a line on concrete surface (length 1,5m-2,0m) and a testing grid per 100mm is defined.
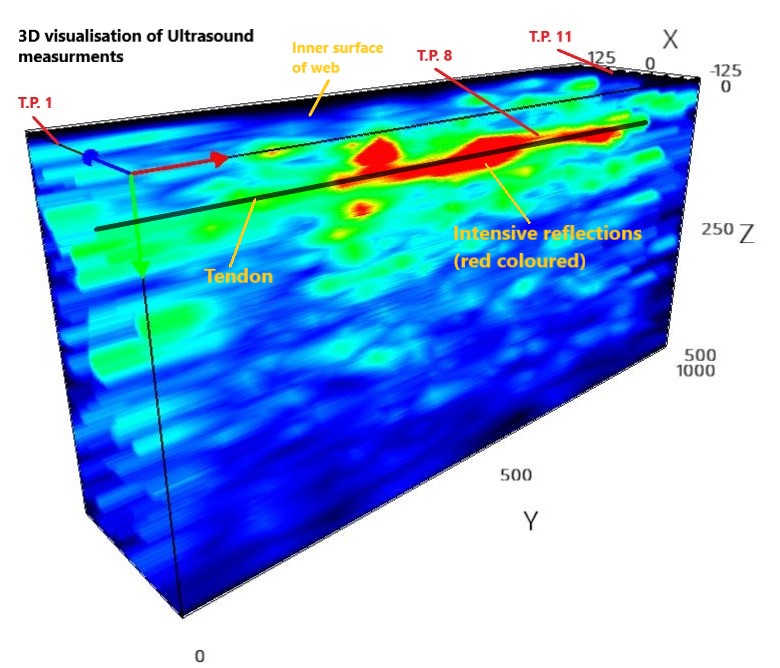
- Then Ultrasound 3D tomography measurements are performed in order to locate suspicious areas (voided) around and inside the duct. Also, by ultrasound measurements (B-scans), the shear velocities of concrete are estimated at several testing positions and the depth of the tendon’s duct.
Following the tomography evaluation, at certain suspicious testing positions, Impact-echo tests are performed in order to estimate the depth and the extent of possible voids around or/and into the duct. The red colored area shown in picture below, indicates a suspicious zone where probably tendon duct is partially or totally empty.
Finally, microdrills and core drillings are executed at the most suspicious testing points in order to evaluate the condition of the ducts. Then, opening of the corrugated metallic ducts is performed by using special tools and injection grout sampling is performed. Also, condition of strands by visual observation is performed and the corrosion class of the strands is evaluated. The aforementioned process is repeated for each duct and according to the insitu findings.



